

Lorazepam and clonazepam have low cross-reactivity and are generally not detected on benzodiazepine IA. 11, 12 This means that benzodiazepines are detected based on their ability to cross-react with the IA test. However, benzodiazepine IAs also can detect other drugs that are structurally similar to benzodiazepines. 4ĪThis table contains commonly used opioids and is not meant to be cpmprehensive.īenzodiazepine IAs often are designed to detect nordiazepam, oxazepam, and temazepam, all of which are metabolites of diazepam. 8, 9 Additional tests may be ordered separately or electronically built into the ordering system for other drugs or drug classes, such as benzodiazepines, barbiturates, lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD), propoxyphene, buprenorphine, tramadol, methadone, fentanyl, and oxycodone. Most automated IAs include the “Federal Five” drugs or drug classes tested for in federal employees, which include marijuana, cocaine, opiates, amphetamines, and phencyclidine (PCP).
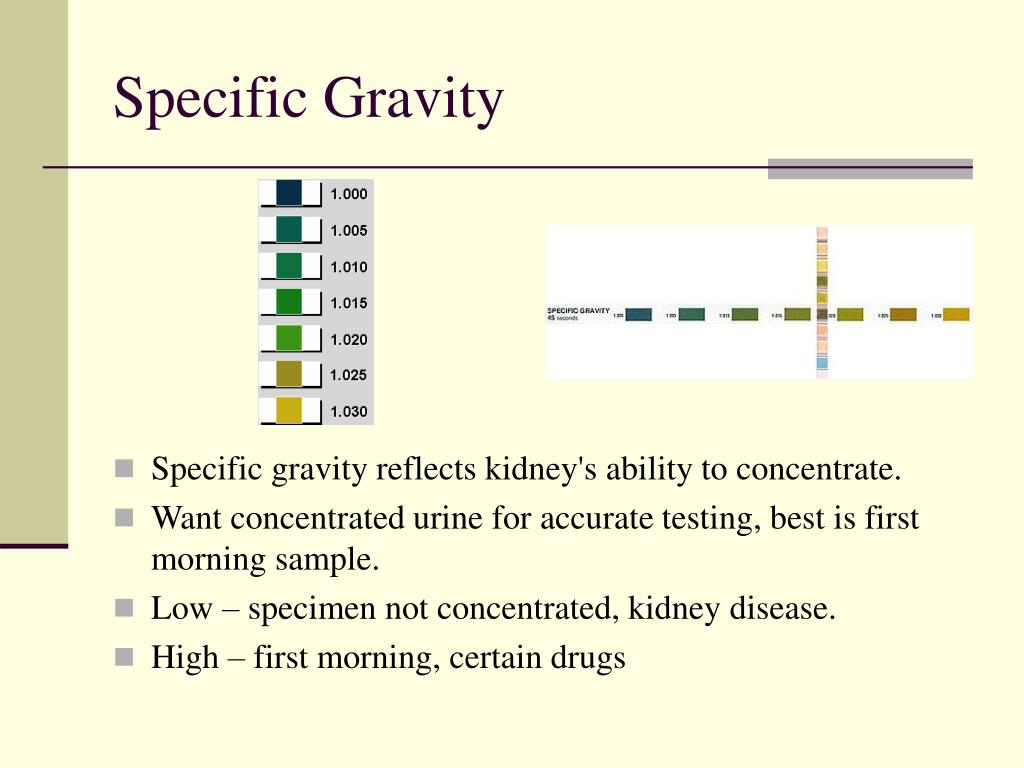
#NORMAL URINE SPECIFIC GRAVITY WINDOWS#
Immunoassay tests also are subject to varying windows of detection depending on the substance ingested ( Table 3). Immunoassay is relatively quick, inexpensive, and sensitive however, because it lacks specificity, it can result in various false positives and false negatives. It also can detect the presence of illegal substances or unprescribed medications. Typically, UDM by IA is performed as an initial evaluation of potential appropriate use, misuse, nonuse, or abuse of medications. 8 Immunoassay monitoring is the initial qualitative test to identify the presence of drug classes in the urine based on a detection threshold. The IA drug test uses antibodies to detect the presence of selected drugs and/or their metabolites based on a predetermined cutoff threshold. Hair follicle testing is an option as well. Although this method is more expensive and invasive, it eliminates means of tampering.
Another approach if tampering is suspected is to collect blood samples. Whenever in doubt, it is advisable that health care providers (HCPs) contact their laboratory to investigate tampering. There are laboratory tests to detect the presence of these adulterants. The active ingredients of some include peroxide/peroxidase, sodium or potassium nitrate, pyridinium chlorochromate, or glutaraldehyde.

10 There are numerous commercially available adulterants, including Klear, UrinAid, Urine Luck, Stealth Synthetics, Whizzies, and Clear Choice. House-hold adulterants include vinegar, detergent, sodium chloride, hydrogen peroxide, eye/nose drops, soda, or ammonia. Other causes of diluted urine should be considered, such as renal tubular dysfunction or diuretic use. Dilution may occur pre-collection by consumption of excess amounts of fluids or post-collection by adding fluid to the specimen. The combination of specific gravity and urinary creatinine may help screen for dilution or substitution. Sending the patient a letter in the mail with test results and discharging the patient from the clinic is not appropriate and could increase risk for substance misuse.
Discuss the test results with patients and address aberrant drug behavior.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
